Despite sanctions, Iranian exporters continue to trade smarter in 2025, exploring new export alternatives, regional rout...
Exploring the Ancient Silk Road: A Journey Along Abrishamroad
Introduction
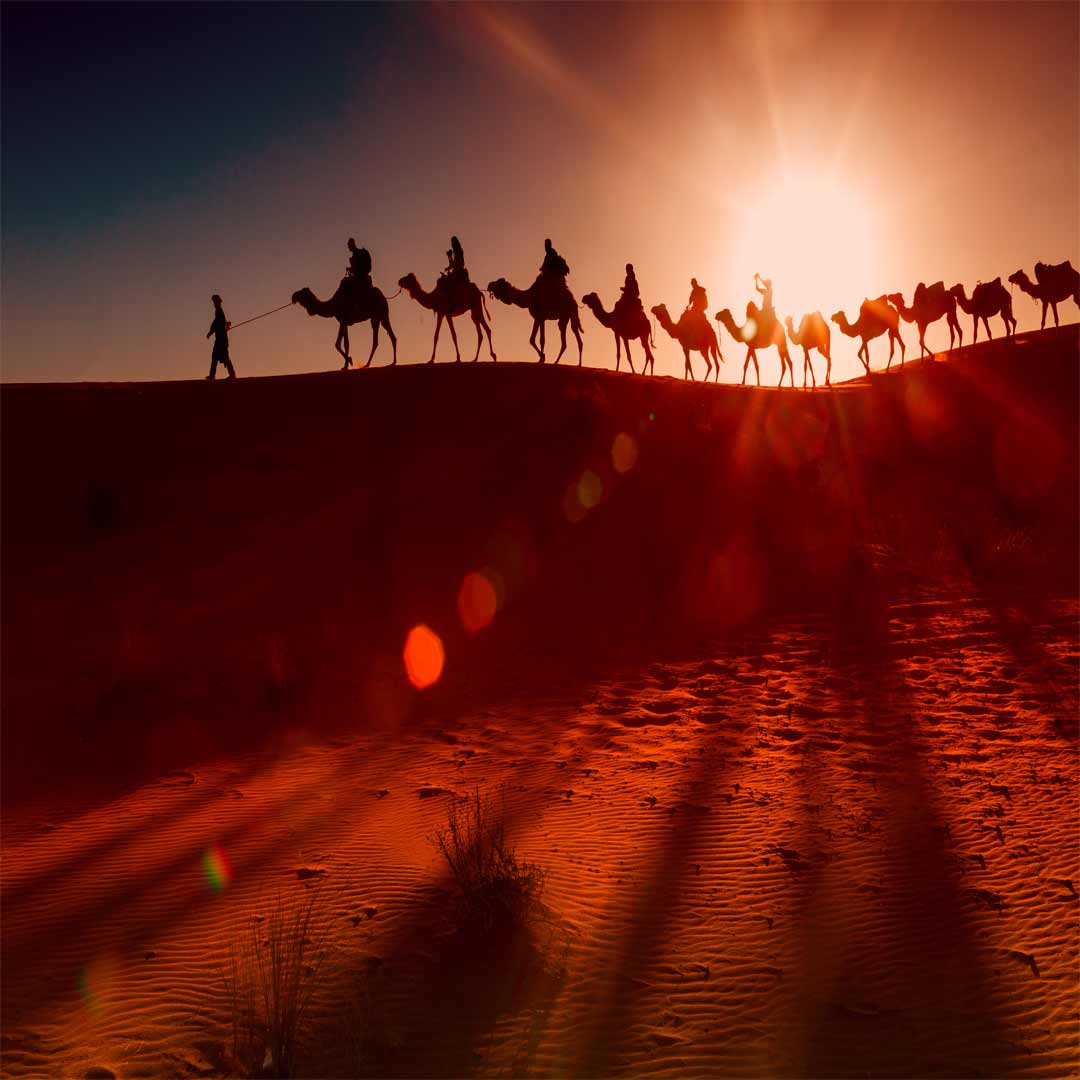

The Silk Road, known as "Abrishamroad" in Persian, was one of the most influential and enduring trade routes in human history. Spanning over 6,000 kilometers, this network of interconnected routes facilitated the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas across Asia, Europe, and Africa for centuries. In this blog, we will delve into the rich history, significance, and legacy of the Silk Road, focusing on its Persian name, “Abrishamroad.”
A Historical Tapestry of Trade and Culture:
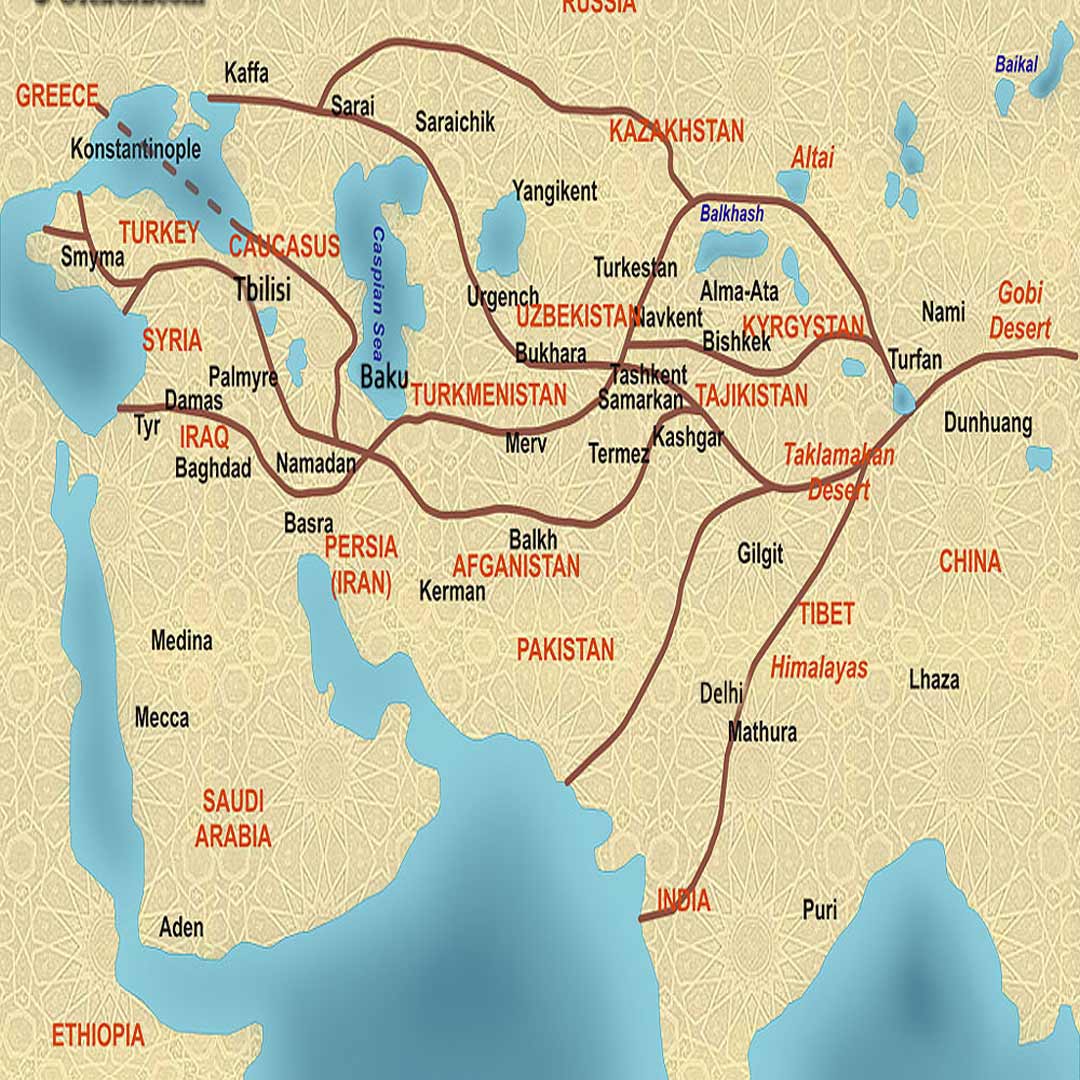
The Silk Road's history dates back more than two millennia. It originated during the Han Dynasty in China, around the 2nd century BCE. The network of routes spanned from the Chinese cities of Xi'an and Dunhuang through Central Asia, Persia (modern-day Iran), the Indian subcontinent, and the Levant, and finally to the Mediterranean. Along these routes, various commodities were traded, including silk, spices, precious metals, gemstones, textiles, and cultural items such as art, music, and religious beliefs.
The Persian Influence on the Silk Road:
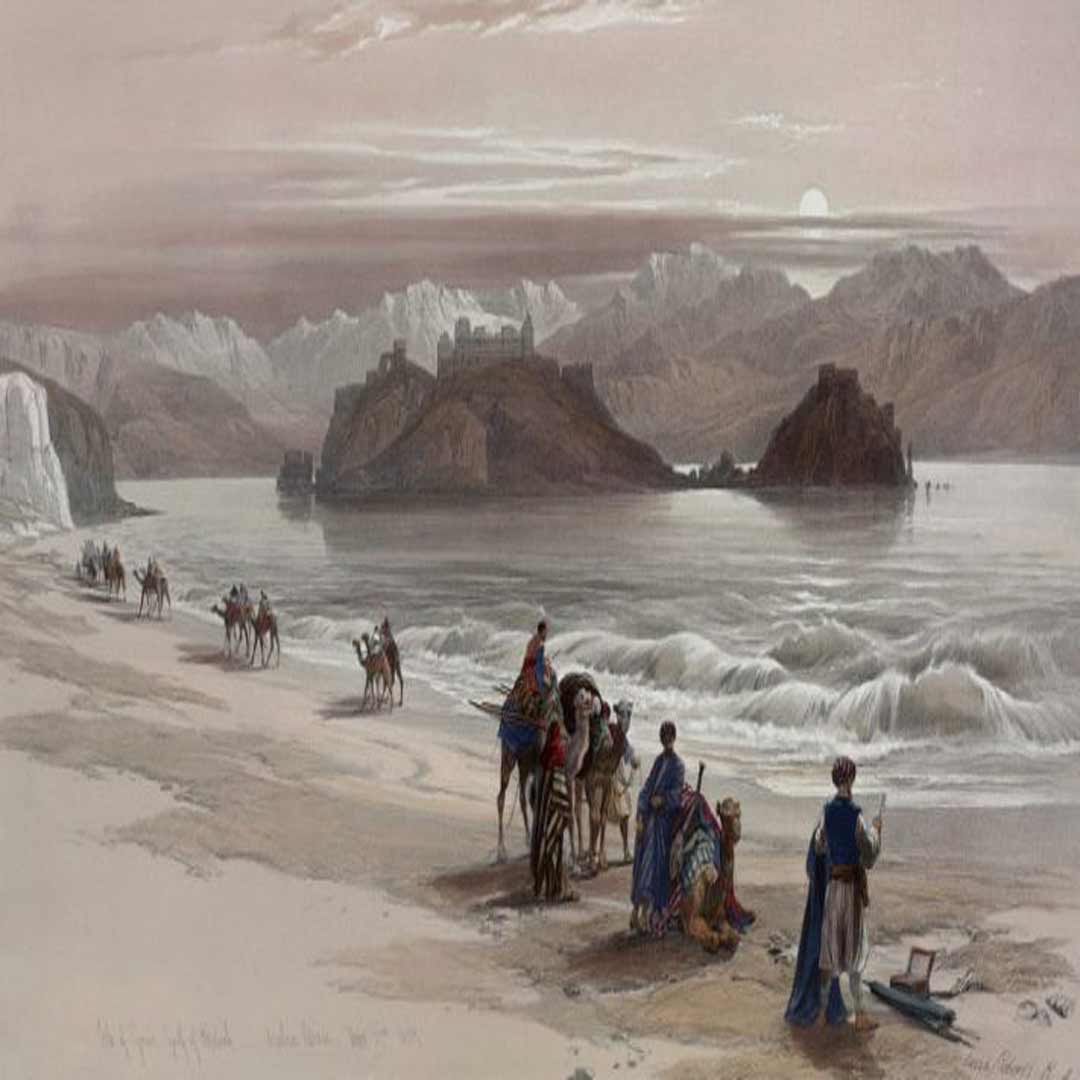

Persia, situated at the crossroads of the Silk Road, played a pivotal role in the exchange of goods and ideas. The Persian Empire, with its advanced infrastructure and centralized administration, facilitated and controlled trade along this historic route. Cities like Isfahan, Tehran, and Shiraz became major trading hubs, fostering the fusion of diverse cultures, languages, and traditions. Persian merchants, scholars, and artisans made significant contributions to the Silk Road's cosmopolitan character.
One of the most sought-after commodities along the Silk Road was Persian silk. Known for its exceptional quality and intricate designs, Persian silk was highly prized across the known world. The term "Abrisham" in the Persian name for the Silk Road, Abrishamroad, directly refers to silk, highlighting its importance in the trade network.
Cultural Exchange Along Abrishamroad:
The Silk Road was not merely a conduit for material goods; it was a melting pot of cultures and ideas. Travelers, scholars, and merchants exchanged not only products but also knowledge and philosophies. scholars such as Avicenna (Ibn Sina) made remarkable contributions to medicine and philosophy, which spread along the Silk Road. The Persian language, too, left its mark, becoming a lingua franca for communication across different regions.
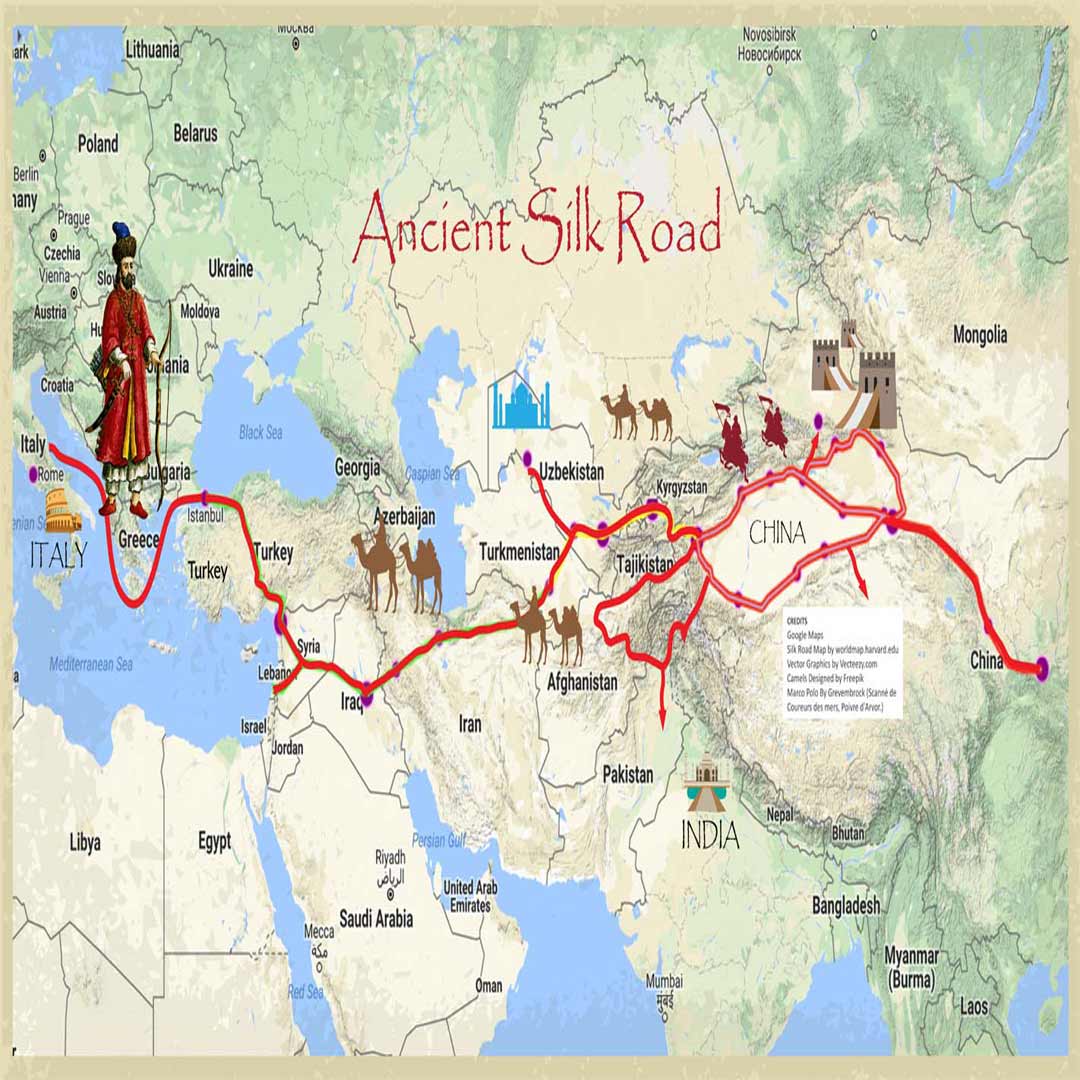
The Legacy of Abrishamroad:
While the Silk Road saw its decline due to the discovery of maritime routes and political upheavals, its legacy endures in the modern world. The exchange of cultures, religions, art, and technology along the Silk Road laid the groundwork for our globalized society. The historical significance of Abrishamroad in shaping our modern world cannot be overstated. Today, initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) led by China aim to revive and expand the concept of interconnected trade routes, recalling the spirit of the Silk Road. The ancient network's spirit continues to inspire nations to collaborate on infrastructure projects that enhance trade and cultural exchange.
Conclusion: The Silk Road, known as Abrishamroad in Persian, was a testament to human ingenuity and a bridge between the East and West. Its historical significance extends beyond the physical exchange of goods, serving as a symbol of cultural and intellectual exchange. The legacy of the Silk Road is deeply embedded in our modern world, reminding us of the profound impact that cross-cultural interaction can have on the course of history. As we continue to explore our shared global heritage, we must never forget the remarkable contributions and enduring legacy of Abrishamroad.




